Circadian Rhythm – Why following our Natural Biological Clock is beneficial for our health
Written by Dr. Khushboo Gadda
Graphics by Ria Gorey
Share this article
Key points
- How the Circadian Rhythm is controlled.
- Assumptions about circadian rhythm around the influence of the sun.
- Factors helping reset our chronobiological clock- sunlight, food, the temperature of surroundings, social interactions.
- Understanding your circadian rhythm by the timings and utilize it to optimize your productivity and health.
- Circadian fasting- the role of hormones around the rhythm, using it to our advantage for eating the right food at the right time.
When our planet rotates on its axis, it takes approximately 24 hours to complete one rotation. So right from the big bang and when life started on planet earth, every living organism follows a natural 24-hour sleep-wake cycle- right from microbes to mammals. Human beings are no different. When our ancestors used to live in forests, they had no clock to tell the time. In fact, time as a concept was invented only in 1500 BC by the Egyptians. They used to tell time by the position of the Sun in the sky. So, it is natural to assume that the sun controls our circadian rhythm.
Circadian (Latin circa ‘about’ + dies ‘day’) rhythm- is a 24-hour sleep-wake cycle that we all follow. Until a few years ago, it was believed that the sun controls our sleep-wake cycle. Therefore, a few scientists experimented by going to the caves and blocking sunlight for 32 days.
At the end of the period, they found that they could wake up and sleep simultaneously every day. So this proved that the circadian rhythm does not depend upon the sun’s rays. (The countries which get less sunlight throughout the day can therefore still have fully functioning citizens).
Sunlight is a facilitator to boost our hormone levels. However, it does not play a vital role.

Let’s dive a little deeper into the circadian rhythm:
A. How is it controlled?
Our brain itself controls it. Our brain releases certain chemicals throughout the day, which helps us feel alert/sleepy/energetic,/lazy. These chemicals are released particularly at certain times of the day and help regulate every body’s function.
B. Rise and shine, young lady!
Before we wake up, there is a spike of norepinephrine (adrenaline) inside our body which helps us rise. This spike (if our schedule is regular) occurs at a particular time in the morning.
C. The Circadian Rhythm is not precisely 24 hours
It is around 24 hours- 15 minutes. Although the sun is not an essential factor for our circadian rhythm (so blind individuals do not lose their circadian rhythms), it is one of the factors which help in resetting our chronobiological clock. Other factors are- food, the temperature of surroundings, social interactions we do.
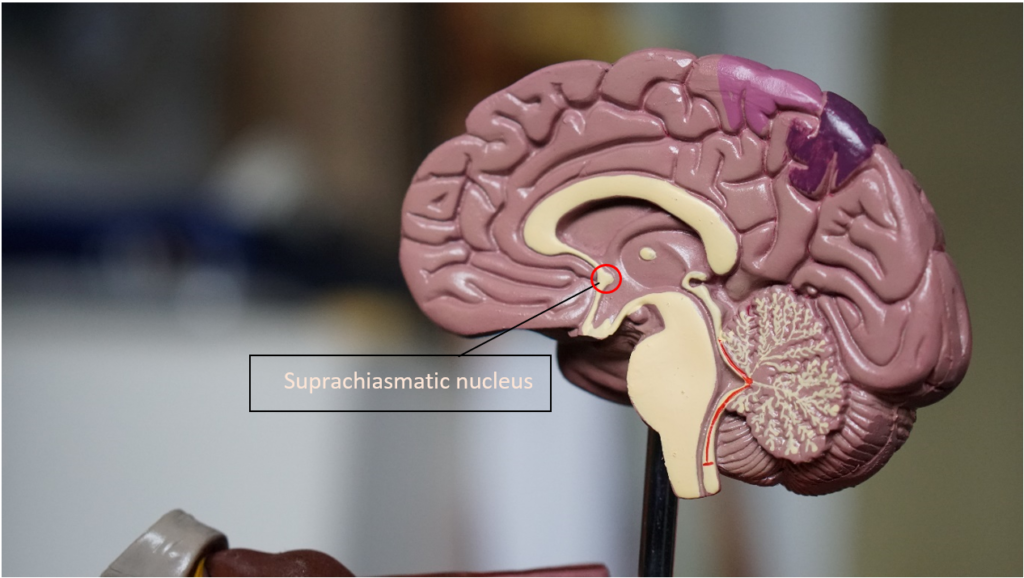
1. Sunlight– In the morning, opening up the window for sun rays to come in, the sunlight hits our suprachiasmatic nucleus, which is present just behind our eyes. This nucleus uses visual input from the lights to help us become alert as we wake up slowly- even more than the alarm clock or coffee does.
2. Food– The food we eat causes hormones like insulin, melatonin, thyroid hormone, neurotransmitters like serotonin, oxytocin, dopamine, and vasopressin. Insulin, in particular, is connected very importantly to diabetes and insulin resistance in PCOS (the leading causes for non-communicable diseases) and is secreted the most during our active hours. The concept of circadian fasting is to eat the most calories when we are most active so that there is no unnecessary insulin spike in the latter part of the day.

3. The temperature of the surroundings- Our body’s core temperature rises when we wake up in the morning (37.2 degrees Celsius) and drops as we approach bedtime (36.1 degrees Celsius). This temperature drop is essential for our body to fall asleep. Hence, having cool surroundings during bedtime or bathing with warm water at night helps us fall asleep quicker. It causes full-body peripheral vasodilatation, which allows us to cool our core body temperature.
4. Social interactions– Having a highly stimulating or engaging conversation during the daytime can help you have a high alert state which can cause you to be more productive during the day. On the contrary, having fewer social interactions at night or calm, soothing surroundings can help us fall asleep faster.

D. The time factor
The timings given above are reference values, but they can differ from person to person.Let’s say you wake up daily at 6 am. So before that time, there is an adrenaline spike that happens in our body and causes us to wake up.
Now 6 am to 9 am is a time when our body is trying to wake up naturally. You can be listening to spiritual songs or having your regular morning routine in place. You can also fit in a fasted, low-intensity workout.
Between 8 to 9 am, you have a balanced breakfast, which causes an insulin release in your body. A balanced and healthy breakfast will help insulin deliver all the nutrients – carbohydrates, proteins, and fats to the different cells and organs of the body.
From 9 am to 12 pm will be your high alert, high cognitive state. This is a time when you should be doing all your critical, complex, and engaging work. This will help you to be optimally productive and complete your tasks.
Now suppose after a 4-5 hour gap you have your lunch between 12 noon to 1 pm. This is when serotonin gets released and causes you to go into a relaxed state. So the time between 12 pm to 3 pm will be low energy. This is when it is important not to unnecessarily push your mind and body to do heavy tasks and instead take it easy and do some light work or even take a short nap.
From 3 pm to 6 pm or 7 pm is a time for a high-energy state. Fitting in a high-intensity workout can be highly beneficial, and having your last meal is vital as the insulin levels will slowly start to fall after this.
After this time it is important to keep away your gadgets and blue lights at least 2 hours before falling asleep as melatonin- the sleepy hormone secreted by the pineal gland will be thrown off track into understanding that it is still daytime by the suprachiasmatic nucleus.
E. Circadian Fasting

As Indians, we have the privilege of having a circadian fasting ritual deep into our cultures. We stop eating after sunset and give our body a 12-14 hour break, and then consume our maximum calories during the daytime when we are most active. This benefits our hormones and enzymes for digestion tremendously.
Insulin is secreted at a particular time every day, and the chances of our body developing insulin resistance reduces. There is also the factor that having a fast for 12-14 hours in a day gives our chance to use the energy sources from the stored fat and glycogen in the liver. This can reduce central obesity, fatty liver and also reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. It has also been shown to reduce the total plasma cholesterol and triglyceride levels effects on avoiding cancer risk factors such as abnormal cell proliferation and metastasis.
This is a significant reason why stress levels have increased; cravings for unhealthy food and a sedentary lifestyle can also be why. Non-communicable diseases have been showing up on the surface for the past century. It is said that every year 10million+ individuals in India alone are detected with type 2 diabetes. Indeed this is a global problem and is even more dangerous than the Covid-19 Pandemic.
It all comes down to how we live our lives and how much we listen to our bodies. Things which we can control and change in our lifestyle are essential. We can start by following our body’s natural circadian rhythm and changing our habits at the root level.
Contributors

DR. KHUSHBOO GADDA
Guest Writer

RIA GOREY
Multimedia Team
Share this article
[/um_show_content]
